Fabry disease:
Treatment landscape
Sanofi’s commitment to the Fabry community
Sanofi’s ongoing commitment to patients with Fabry disease spans more than 2 decades.
About Fabry disease
Fabry disease is a rare, inherited LSD with heterogeneous multi-organ manifestations for males and females.1-3 In Fabry disease, GL-3 and lyso-GL-3 accumulate in the lysosomes, which can lead to debilitating symptoms and potentially life-threatening complications.4
Fabry disease has an X-linked inheritance pattern1
When one person is diagnosed with Fabry disease, additional family members may also be affected; therefore, family testing is advised following a confirmed diagnosis.6
A closer look at Fabry disease in women
Females with Fabry9 have a higher occurrence of serious complications than females in the general population.3
11x higher risk of end-stage renal disease (ESRD)3,10
7x higher risk of cerebrovascular white matter lesions11,12
4x higher risk of stroke/transient ischemic attack13,14
2x higher risk of left ventricular hypertrophy15,16
Due to tissue-specific X-inactivation, females may have near-normal levels of α-Gal A in plasma and leukocytes yet still present with clinical manifestations.3,17Females who do not present with the typical signs of Fabry disease can still be at risk for severe complications in specific organ systems.3 |
A-Gal A deficiency allows the substrates GL-3 and lyso-GL-3 to accumulate in tissues throughout the body18
As Fabry disease progresses, the risk of severe complications increases4
With progression, Fabry disease can affect organ systems and cause life-threatening complications.4
Cerebrovascular
Stroke and transient
ischemic attack19
Renal
Chronic kidney disease and ESRD
requiring dialysis or transplant3,20
Cardiac
Myocardial inflammation,
myocardial fibrosis, left
ventricular hypertrophy,
heart failure, arrhythmias21
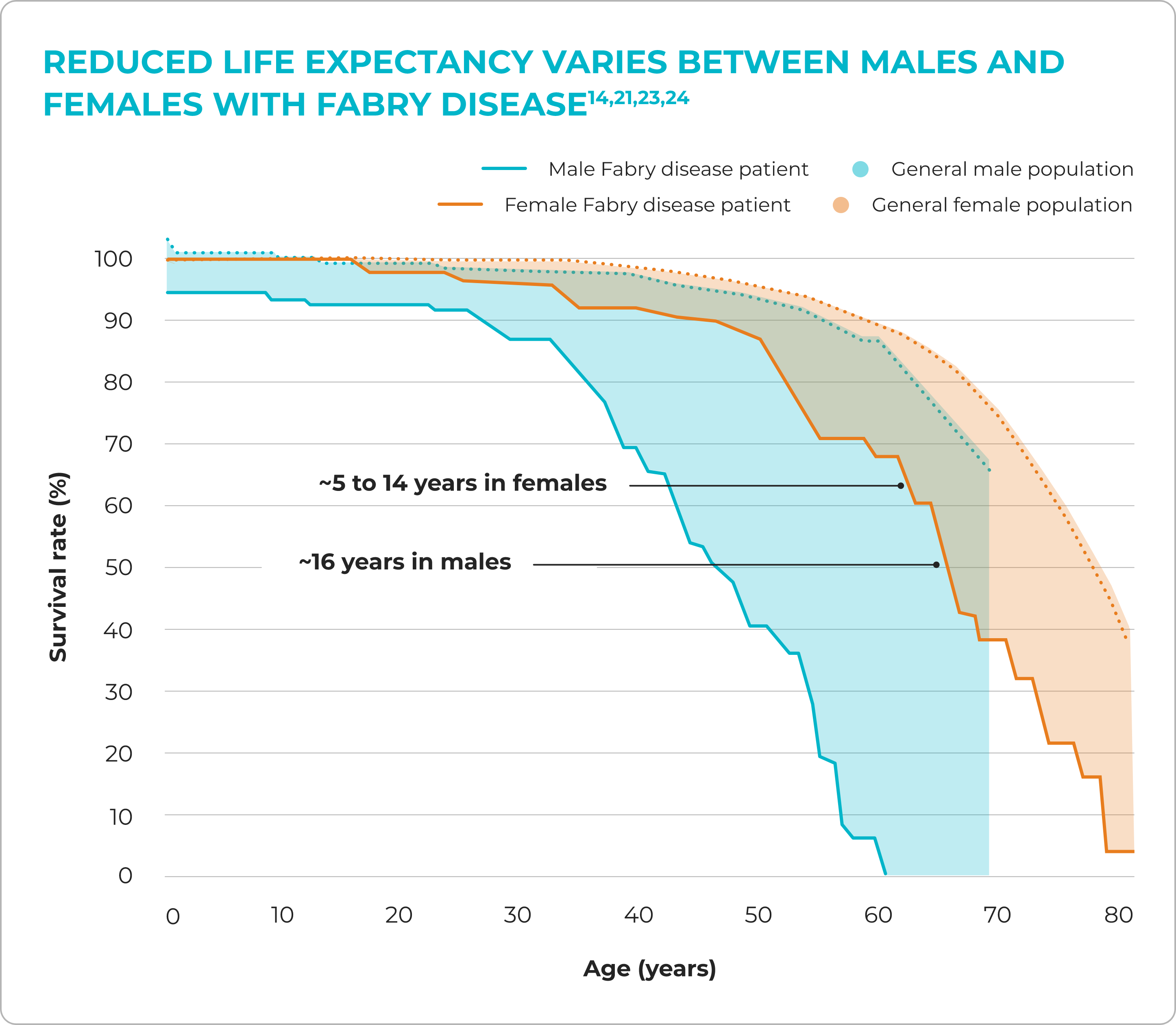
Without disease management, Fabry can significantly reduce life expectancy20
Diagnostic delays of ~15 years can also occur3
α-Gal A, alpha-galactosidase A; GL-3, globotriaosylceramide; GLA, galactosidase A; lyso-GL-3; globotriaosylsphingosine.
References: 1. Germain DP. Fabry disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2010;5:30. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-5-30 2. Germain DP, Waldek S, Banikazemi M, et al. Sustained, long-term renal stabilization after 54 months of agalsidase beta therapy in patients with Fabry disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18(5):1547-1557. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006080816 3. Wilcox WR, Oliveira JP, Hopkin RJ, et al. Females with Fabry disease frequently have major organ involvement: lessons from the Fabry Registry. Mol Genet Metab. 2008;93(2):112-128. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2007.09.013 4. Ortiz A, Germain DP, Desnick RJ, et al. Fabry disease revisited: management and treatment recommendations for adult patients. Mol Genet Metab. 2018;123(4):416-427. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2018.02.014 5. Germain DP, Levade T, Hachulla E, et al. Challenging the traditional approach for interpreting genetic variants: lessons from Fabry disease. Clin Genet. 2022;101(4):390-402. doi:10.1111/cge.14102 6. Laney DA, Fernhoff PM. Diagnosis of Fabry disease via analysis of family history. J Genet Couns. 2008;17(1):79-83. doi:10.1007/s10897-007-9128-x 7. National Institutes of Health. X chromosome. MedlinePlus Genetics. Updated September 28, 2022. Accessed April 3, 2024. https://medlineplus.gov/download/genetics/chromosome/x.pdf 8. X-linked recessive inheritance. Fact sheet. Centre for Genetics Education. Updated
November 2021. Accessed April 3, 2024. https://www.genetics.edu.au/PDF/XLinked_recessive_inheritance_fact_sheet-CGE.pdf 9. Willard HF. The sex chromosomes and X chromosome inactivation. In: Valle DL, Antonarakis S, Ballabio A, Beaudet AL, Mitchell GA, eds. The Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease. McGraw-Hill Education. 2019. Accessed April 3, 2024. https://ommbid.mhmedical.com/content.aspx?bookid=2709§ionid=225078375 10. 2017 USRDS Annual Data Report. United States Renal Data System. 2017. Accessed April 15, 2024.
https://usrds.org/annual-data-report/previousadrs 11. Burlina A, Politei J. The central nervous system involvement in Fabry disease: a review. J Inborn Errors Metab Screen. 2016;4:1-7. doi:10.1177/2326409816661361 12. Fellgiebel A, Müller MJ, Ginsberg L. CNS manifestations of Fabry’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(9):791-795. doi:10.1016/S1474-4422(06)70548-8 13. MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 60 obligate carrier females. J Med Genet. 2001;38(11):769-775. doi:10.1136/jmg.38.11.769 14. Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2017;135(10):e146-e603. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000485 15. Linhart A, Kampmann C, Zamorano JL, et al. Cardiac manifestations of Anderson-Fabry disease: results from the international Fabry outcome survey. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(10):1228-1235. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm153 16. Schirmer H, Lunde P, Rasmussen K. Prevalence of left ventricular hypertrophy in a general population: the Tromsø Study. Eur Heart J. 1999;20(6):429-438. doi:10.1053/euhj.1998.1314 17. Wang RY, Lelis A, Mirocha J, Wilcox WR. Heterozygous Fabry women are not just carriers, but have a significant burden of disease and impaired quality of life. Genet Med. 2007;9(1):34-45. doi:10.1097/gim.0b013e31802d8321 18. Eng CM, Fletcher J, Wilcox WR, et al. Fabry disease: baseline medical characteristics of a cohort of 1765 males and females in the Fabry Registry. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2007;30(2):184-192. doi:10.1007/s10545-007-0521-2 19. Wang G, Zhang Z, Ayala C, Dunet DO, Fang J, George MG. Costs of hospitalization for stroke patients aged 18-64 years in the United States. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23(5):861-868. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.07.017 20. Waldek S, Patel MR, Banikazemi M, Lemay R, Lee P. Life expectancy and cause of death in males and females with Fabry disease: findings from the Fabry Registry. Genet Med. 2009;11(11):790-796. doi:10.1097/GIM.0b013e3181bb05bb 21. Hung CL, Wu YW, Lin CC, et al. 2021 TSOC expert consensus on the clinical features, diagnosis, and clinical management of cardiac manifestations of Fabry disease. Acta Cardiol Sin. 2021;37(4):337-354. doi:10.6515/ACS.202107_37(4).20210601A 22. Mehta A, Clarke JTR, Giugliani R, et al. Natural course of Fabry disease: changing pattern of causes of death in FOS – Fabry Outcome Survey. J Med Genet. 2009;46(8):548-552. doi:10.1136/jmg.2008.065904 23. MacDermot KD, Holmes A, Miners AH. Anderson-Fabry disease: clinical manifestations and impact of disease in a cohort of 98 hemizygous males. J Med Genet. 2001;38(11):750-760.doi:10.1136/jmg.38.11.750 24. Fabrazyme. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation; 2024.
INDICATION AND USAGE
Fabrazyme® is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with confirmed Fabry disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate FABRAZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue FABRAZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine.
Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
In clinical trials and post-marketing experience, approximately 1% of patients developed anaphylactic or severe hypersensitivity reactions, some life-threatening, during Fabrazyme infusion. Reactions have included localized angioedema (including swelling of the face, mouth, and throat), bronchospasm, hypotension, generalized urticaria, dysphagia, rash, dyspnea, flushing, chest discomfort, pruritus, and nasal congestion. Consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids; however, reactions may still occur.
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, some patients developed IgE antibodies or skin test reactivity specific to Fabrazyme.
- Higher incidences of hypersensitivity reactions were observed in adult patients with persistent anti-Fabrazyme antibodies, and in those with high antibody titers compared with antibody negative adult patients.
- Consider testing for IgE antibodies in patients who experienced suspected hypersensitivity reactions and consider the risks and benefits of continued treatment in patients with anti-Fabrazyme IgE antibodies. Rechallenge of these patients should only occur under the direct supervision of qualified personnel, with appropriate medical support measures readily available.
Infusion-Associated Reactions
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, 59% of patients experienced infusion-associated reactions (IARs), some of which were severe. IARs are defined as those occurring on the same day as the infusion. The incidence of these reactions was higher in patients who were positive for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies than those negative for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies.
- Consider pretreatment with antipyretics, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids to reduce the risk of IARs; however, they may still occur.
- If a mild or moderate IAR occurs, consider holding the infusion temporarily, decreasing the infusion rate, and/or reducing the Fabrazyme dosage. If a severe IAR occurs, discontinue Fabrazyme immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment as needed. Assess the risks and benefits of readministering Fabrazyme and monitor patients closely if readministering.
- Patients with advanced Fabry disease may have compromised cardiac function, which may predispose them to a higher risk of severe complications from IARs. Closely monitor patients with compromised cardiac function receiving Fabrazyme.
Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions reported (≥20%) were upper respiratory tract infection, chills, pyrexia, headache, cough, paresthesia, fatigue, peripheral edema, dizziness, and rash.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
INDICATION AND USAGE
Fabrazyme® is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with confirmed Fabry disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate FABRAZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue FABRAZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine.
Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
In clinical trials and post-marketing experience, approximately 1% of patients developed anaphylactic or severe hypersensitivity reactions, some life-threatening, during Fabrazyme infusion. Reactions have included localized angioedema (including swelling of the face, mouth, and throat), bronchospasm, hypotension, generalized urticaria, dysphagia, rash, dyspnea, flushing, chest discomfort, pruritus, and nasal congestion. Consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids; however, reactions may still occur.
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, some patients developed IgE antibodies or skin test reactivity specific to Fabrazyme.
- Higher incidences of hypersensitivity reactions were observed in adult patients with persistent anti-Fabrazyme antibodies, and in those with high antibody titers compared with antibody negative adult patients.
- Consider testing for IgE antibodies in patients who experienced suspected hypersensitivity reactions and consider the risks and benefits of continued treatment in patients with anti-Fabrazyme IgE antibodies. Rechallenge of these patients should only occur under the direct supervision of qualified personnel, with appropriate medical support measures readily available.
Infusion-Associated Reactions
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, 59% of patients experienced infusion-associated reactions (IARs), some of which were severe. IARs are defined as those occurring on the same day as the infusion. The incidence of these reactions was higher in patients who were positive for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies than those negative for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies.
- Consider pretreatment with antipyretics, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids to reduce the risk of IARs; however, they may still occur.
- If a mild or moderate IAR occurs, consider holding the infusion temporarily, decreasing the infusion rate, and/or reducing the Fabrazyme dosage. If a severe IAR occurs, discontinue Fabrazyme immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment as needed. Assess the risks and benefits of readministering Fabrazyme and monitor patients closely if readministering.
- Patients with advanced Fabry disease may have compromised cardiac function, which may predispose them to a higher risk of severe complications from IARs. Closely monitor patients with compromised cardiac function receiving Fabrazyme.
Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions reported (≥20%) were upper respiratory tract infection, chills, pyrexia, headache, cough, paresthesia, fatigue, peripheral edema, dizziness, and rash.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
INDICATION AND USAGE
Fabrazyme® is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with confirmed Fabry disease.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate FABRAZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g. anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue FABRAZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine.
Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis
In clinical trials and post-marketing experience, approximately 1% of patients developed anaphylactic or severe hypersensitivity reactions, some life-threatening, during Fabrazyme infusion. Reactions have included localized angioedema (including swelling of the face, mouth, and throat), bronchospasm, hypotension, generalized urticaria, dysphagia, rash, dyspnea, flushing, chest discomfort, pruritus, and nasal congestion. Consider pretreating with antihistamines, antipyretics, and/or corticosteroids; however, reactions may still occur.
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, some patients developed IgE antibodies or skin test reactivity specific to Fabrazyme.
- Higher incidences of hypersensitivity reactions were observed in adult patients with persistent anti-Fabrazyme antibodies, and in those with high antibody titers compared with antibody negative adult patients.
- Consider testing for IgE antibodies in patients who experienced suspected hypersensitivity reactions and consider the risks and benefits of continued treatment in patients with anti-Fabrazyme IgE antibodies. Rechallenge of these patients should only occur under the direct supervision of qualified personnel, with appropriate medical support measures readily available.
Infusion-Associated Reactions
In Fabrazyme clinical trials, 59% of patients experienced infusion-associated reactions (IARs), some of which were severe. IARs are defined as those occurring on the same day as the infusion. The incidence of these reactions was higher in patients who were positive for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies than those negative for anti-Fabrazyme antibodies.
- Consider pretreatment with antipyretics, antihistamines, and/or corticosteroids to reduce the risk of IARs; however, they may still occur.
- If a mild or moderate IAR occurs, consider holding the infusion temporarily, decreasing the infusion rate, and/or reducing the Fabrazyme dosage. If a severe IAR occurs, discontinue Fabrazyme immediately and initiate appropriate medical treatment as needed. Assess the risks and benefits of readministering Fabrazyme and monitor patients closely if readministering.
- Patients with advanced Fabry disease may have compromised cardiac function, which may predispose them to a higher risk of severe complications from IARs. Closely monitor patients with compromised cardiac function receiving Fabrazyme.
Common Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions reported (≥20%) were upper respiratory tract infection, chills, pyrexia, headache, cough, paresthesia, fatigue, peripheral edema, dizziness, and rash.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
This site is intended for US payers only.
© Sanofi. All rights reserved.
Fabrazyme and Sanofi are registered trademarks of Sanofi or an affiliate.
CareConnect Personalized Support Services is a trademark of Sanofi or an affiliate.