DUPIXENT® in moderate-to-severe eosinophilic or OCS-dependent asthma
Patients aged 6+ years
THE ONLY BIOLOGIC INDICATED FOR PATIENTS WITH OCS-DEPENDENT ASTHMA1
DUPIXENT STUDIES ENROLLED MODERATE-TO-SEVERE ASTHMA (EOSINOPHILIC OR OCS-DEPENDENT) PATIENTS2-8

Adults aged
18 years and older
Adolescents aged
12 to 17 years

Children aged
6 to 11 years
Efficacy in asthma: Adult/adolescent patients7
DUPIXENT demonstrated the ability to reduce severe exacerbations in adult/adolescent patients with moderate-to-severe asthma (eosinophilic or dependent on oral corticosteroids).
Severe exacerbations
TRAVERSE OLE results are descriptive. Definitive conclusions cannot be made. Data were not multiplicity controlled, and there are limitations associated with an open-label study design, including the lack of comparator arm, a decreasing sample size, and potential continued involvement of responders and attrition of non-responders.
In QUEST, no statistically significant differences were observed during the 52-week treatment period in patients with baseline blood eosinophils <150 cells/μL taking DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W or 300 mg Q2W + standard of care and in the ≥150 to <300 cells/μL eosinophil subgroup treated with DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W + standard of care vs matching placebo + standard of care.
aSevere exacerbations were defined as deterioration of asthma requiring the use of systemic corticosteroids for at least 3 days or hospitalization or an ED visit due to asthma requiring systemic corticosteroids.
bBaseline blood eosinophil level ≥300 cells/μL (DRI12544, secondary endpoint).
cAnalysis includes DRI12544 and QUEST patients enrolled in TRAVERSE.
dOf the 542 patients who experienced at least 1 severe asthma exacerbation, 66 (3.2% of the overall study population) had an exacerbation requiring hospitalization or an ED visit during the TRAVERSE study period (unadjusted annualized event rate of 0.027).
e79.5% of patients rolled over from DRI12544 (n=396) experienced 0 exacerbations during Weeks 48 to 96.
f74% of patients rolled over from DRI12544 and QUEST (n=2062) experienced 0 exacerbations over ~3 years of treatment with DUPIXENT.
Lung function
TRAVERSE OLE results are descriptive. Definitive conclusions cannot be made. Data were not multiplicity controlled, and there are limitations associated with an open-label study design, including the lack of comparator arm, a decreasing sample size, and potential continued involvement of responders and attrition of non-responders.
a178 L was the baseline FEV1 level from QUEST (n=633) compared with a placebo value of 1.75 L (n=321).
bFEV1 was assessed in the exposed population (observed cases) using descriptive statistics.
OCS/SCS use
TRAVERSE OLE results are descriptive. Definitive conclusions cannot be made. Data were not multiplicity controlled, and there are limitations associated with an open-label study design, including the lack of comparator arm, a decreasing sample size, and potential continued involvement of responders and attrition of non-responders.
aOCS reduction was at the investigator’s discretion.
CI, confidence interval; ED, emergency department; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; ITT, intention to treat; LSM, least squares mean; OCS, oral corticosteroid; OLE, open-label extension; Q2W, once every 2 weeks; SCS, systemic corticosteroid.
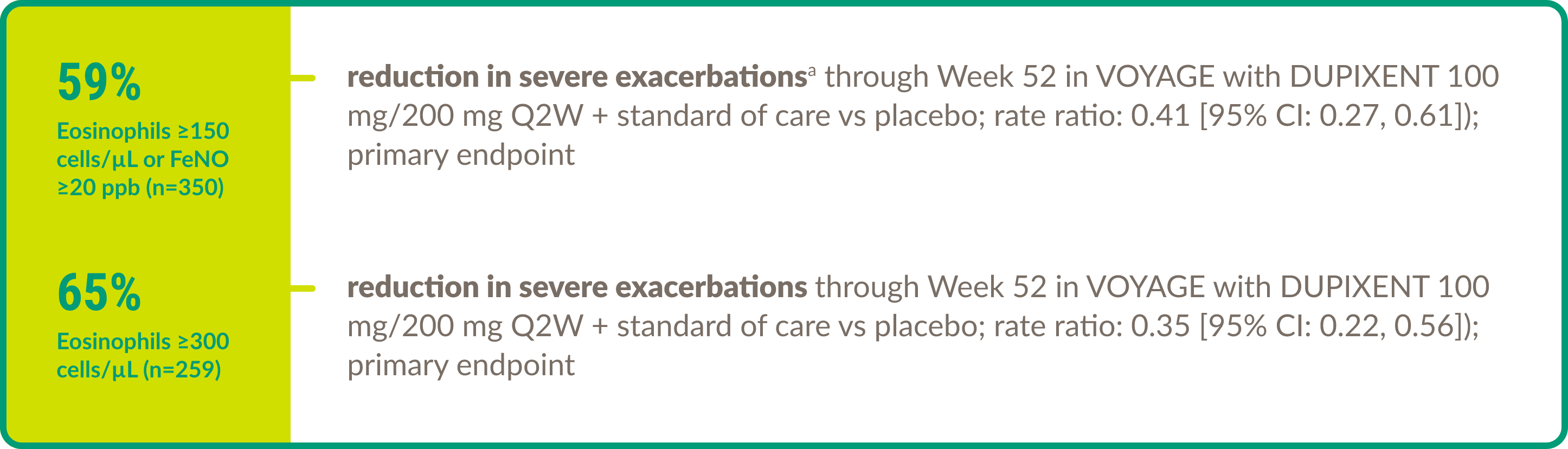
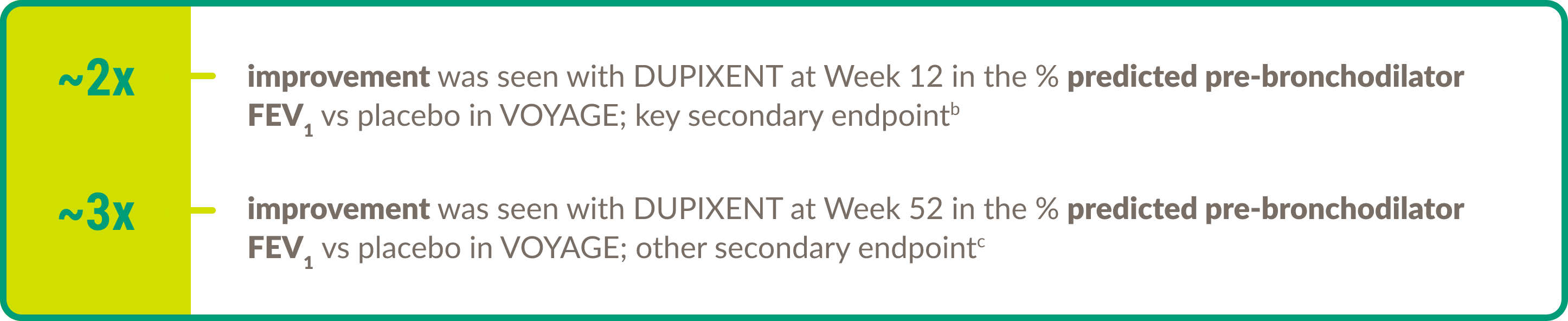
Efficacy in asthma: Pediatric patients
DUPIXENT demonstrated efficacy in the following key areas of asthma control in children aged 6 to 11 years with moderate-to-severe asthma (eosinophilic or OCS–dependent).
Severe exacerbations7,8
Lung function8
OCS/SCS use7,8
Weight-based dosing: DUPIXENT 100 mg Q2W (<30 kg) or 200 mg Q2W (≥30 kg).8
The safety results of DUPIXENT observed in children through Week 52 were similar to the safety profile identified from studies in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe asthma as well as parasitic (helminth) infections.1
aSevere exacerbations were defined as deterioration of asthma requiring the use of SCSs for at least 3 days or hospitalization or an ED visit due to asthma requiring SCSs.8
b5.21% improvement in the % predicted pre-bronchodilator FEV1 in children with eosinophils ≥150 cells/μL or FeNO ≥20 ppb (n=236) (eosinophilic phenotype) at Week 12 with DUPIXENT 100 mg/200 mg Q2W + standard of care vs placebo + standard of care (n=114); 5.32% improvement in the % predicted pre-bronchodilator FEV1 in children with eosinophils ≥300 cells/μL (n=175) at Week 12 with DUPIXENT 100 mg/200 mg Q2W + standard of care vs placebo + standard of care (n=84).9
c7.79% improvement in the % predicted pre-bronchodilator FEV1 in children with eosinophils ≥150 cells/μL or FeNO ≥20 ppb (n=236) (eosinophilic phenotype) at Week 52 with DUPIXENT 100 mg/200 mg Q2W + standard of care vs placebo + standard of care (n=114); 8.35% improvement in the % predicted pre-bronchodilator FEV1 in children with eosinophils ≥300 cells/μL (n=175) at Week 52 with DUPIXENT 100 mg/200 mg Q2W + standard of care vs placebo + standard of care (n=84).9
FeNO, fractional exhaled nitric oxide; GINA, Global Initiative for Asthma; ppb, parts per billion.
Safety profile in asthma
The safety profile of DUPIXENT in asthma has been studied in nearly 3000 patients
ADVERSE REACTIONS OCCURRING IN ≥1% OF PATIENTS ON DUPIXENT + STANDARD OF CARE AT HIGHER RATES THAN THOSE OBSERVED WITH PLACEBO + STANDARD OF CARE IN DRI2544 and QUEST (6-MONTH SAFETY POOL)1,A
|
ADVERSE REACTION |
DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W + STANDARD OF CARE |
DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W + STANDARD OF CARE |
PLACEBO + STANDARD OF CARE |
|
Injection site reactionsb |
111 (14) |
144 (18) |
50 (6) |
|
Oropharyngeal pain |
13 (2) |
19 (2) |
7 (1) |
|
Eosinophiliac |
17 (2) |
16 (2) |
2 (<1) |
In DRI12544 and QUEST, the percentages of patients who discontinued treatment due to adverse events were 4% in the placebo + standard of care group, 3% in the DUPIXENT 200 mg Q2W + standard of care group, and 6% in the DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + standard of care group.1
The safety results of DUPIXENT observed in children through Week 52 were similar to the safety profile identified from studies in adults and adolescents with moderate-to-severe asthma as well as parasitic (helminth) infections.1
DUPIXENT demonstrated a long-term safety profile up to 96 weeks in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma.6,d
The TRAVERSE OLE primary endpoint results are as follows: 86% of patients enrolled from DRI12544, 79% of patients enrolled from QUEST, and 77% of patients enrolled from VENTURE experienced at least 1 treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) up to Week 96 of the OLE period.7
aThe safety population (DRI12544 and QUEST) included patients aged 12 to 87 years; 63% were female, and 82% were White. DUPIXENT 200 mg or 300 mg was administered subcutaneously Q2W following an initial dose of 400 mg or 600 mg, respectively.1
bInjection site reactions cluster includes erythema, edema, pruritus, pain, and inflammation.1
cNone met the criteria for serious eosinophilic conditions.1
DUPIXENT has a demonstrated safety profile in asthma patients requiring OCS5
Adverse events occurring in ≥5% of patients in either group in VENTUREa
|
ADVERSE EVENT |
DUPIXENT 300 mg Q2W + STANDARD OF CARE |
PLACEBO + STANDARD OF CARE |
|
Viral upper respiratory tract infection |
9 (9%) |
19 (18%) |
|
Bronchitis |
7 (7%) |
6 (6%) |
|
Sinusitis |
7 (7%) |
4 (4%) |
|
Influenza |
3 (3%) |
6 (6%) |
|
Eosinophiliab |
14 (14%) |
1 (1%) |
|
Injection site reactionc |
9 (9%) |
4 (4%) |
|
≥ 1 measurement of a blood |
13 (13%) |
1 (1%) |
The safety population (VENTURE) included all patients who received at least 1 dose or a partial dose of DUPIXENT or placebo; data were analyzed according to the regimen received.
aAdverse events in this category were reported according to preferred terms in the Medical Dictionary for Regulatory Activities (MedDRA), version 20.0.
bThe adverse event of eosinophilia in this table is a combination of the preferred items of an eosinophil count increase (in 7% of the patients in the DUPIXENT group vs no patients in the placebo group) and eosinophilia (7% vs 1%).
cInjection site reaction is a high-level term in MedDRA.
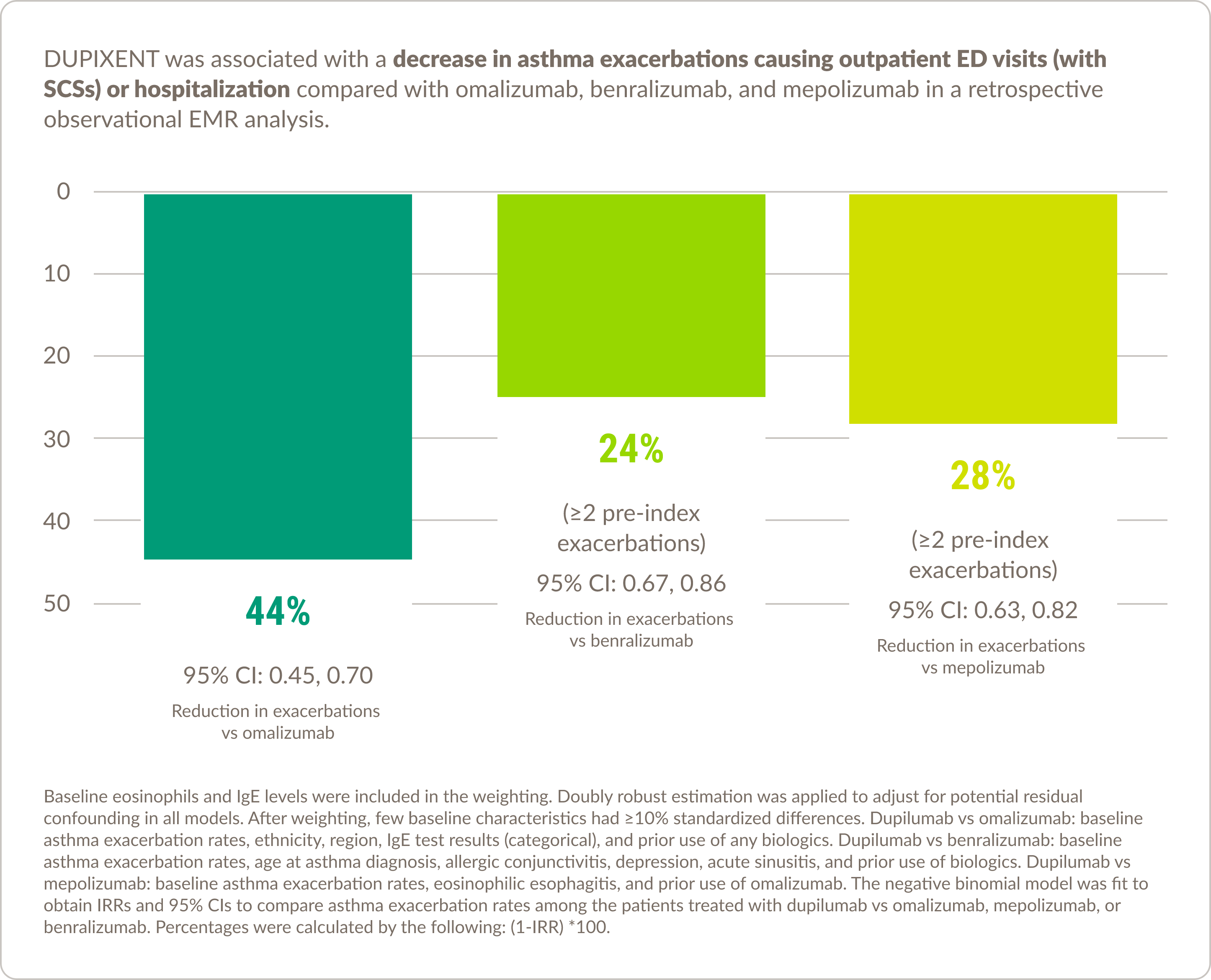
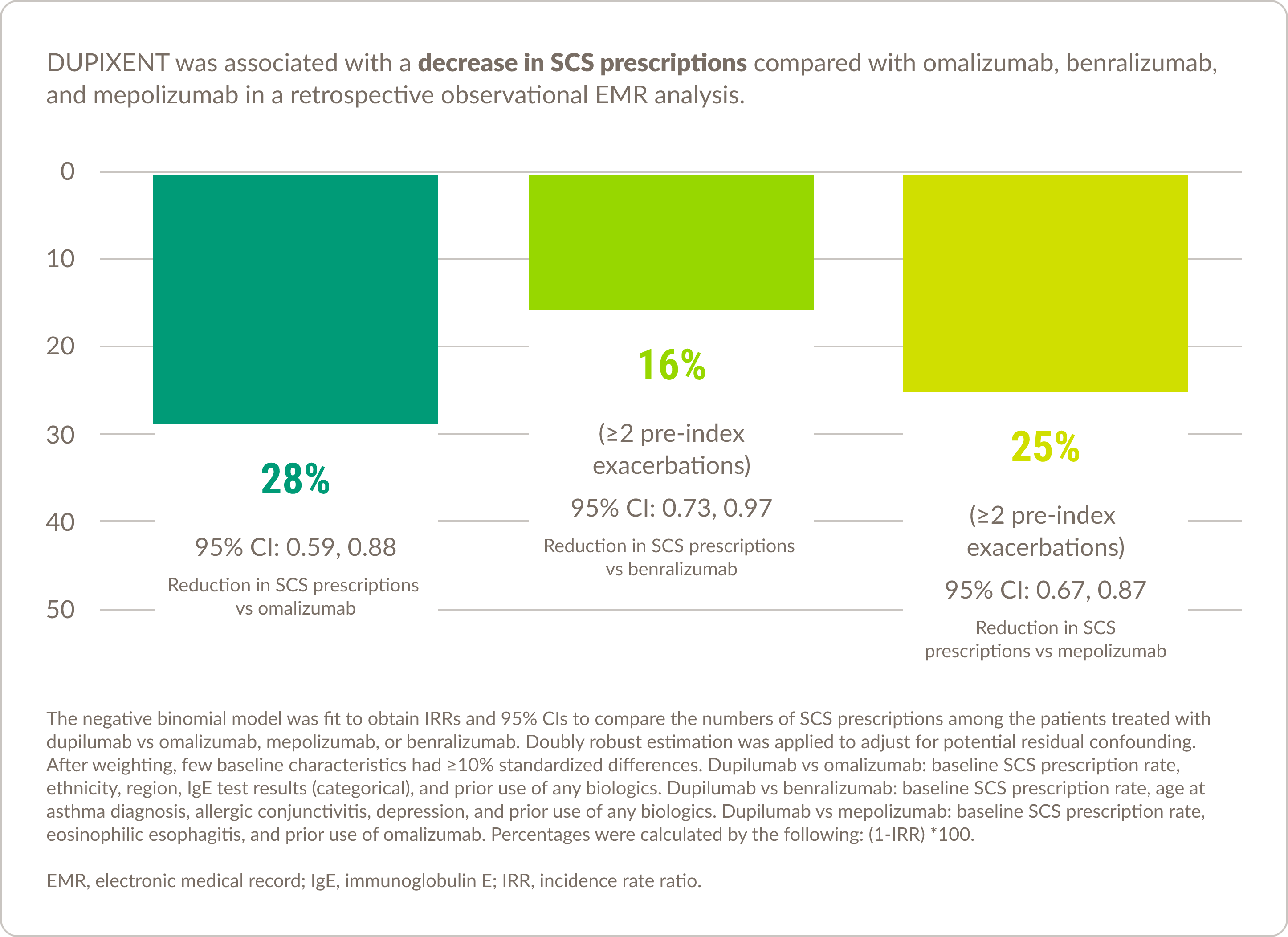
Real-world experience in asthma10
DUPIXENT was associated with decreased healthcare resource utilization compared with other biologic therapies
Please note that there are currently no prospective, randomized, double-blind, head-to-head studies comparing DUPIXENT with other asthma biologics available, and the results of this study should be interpreted within the limitations of the EMR data.
Limitations
![]() The asthma exacerbation definition used in this analysis has been validated in the literature and aligns with the dupilumab Phase 3 QUEST trial; however, due to differences in study design and data limitations on OCS use in hospitalized patients, observed asthma exacerbations may differ from what was observed in the clinical trials
The asthma exacerbation definition used in this analysis has been validated in the literature and aligns with the dupilumab Phase 3 QUEST trial; however, due to differences in study design and data limitations on OCS use in hospitalized patients, observed asthma exacerbations may differ from what was observed in the clinical trials
![]()
These results should be interpreted within the limitations of EMR data10
![]() The potential for bias from residual or unmeasured confounding variables that influenced the choice of treatment and endpoints of interest may not have been captured in the TriNetX EMR database7
The potential for bias from residual or unmeasured confounding variables that influenced the choice of treatment and endpoints of interest may not have been captured in the TriNetX EMR database7
![]() Baseline comorbidities in patients from the study sample were identified by diagnosis codes in the EMR, which may be incomplete; therefore, misclassification due to miscoding of these conditions may have occurred7
Baseline comorbidities in patients from the study sample were identified by diagnosis codes in the EMR, which may be incomplete; therefore, misclassification due to miscoding of these conditions may have occurred7
![]() Prescription drug data reflected drugs that were prescribed and not those that were actually filled and/or taken. For example, although patients may have had prescriptions for systemic corticosteroids, they may not have taken them as prescribed or at all7
Prescription drug data reflected drugs that were prescribed and not those that were actually filled and/or taken. For example, although patients may have had prescriptions for systemic corticosteroids, they may not have taken them as prescribed or at all7
![]() Missing information in medical records for some variables and a lack of information on patient care received at outside institutions may have resulted in the underreporting of treatments and clinical tests, which are limitations of real-world data. However, these inconsistencies presumably affected all cohorts equally7
Missing information in medical records for some variables and a lack of information on patient care received at outside institutions may have resulted in the underreporting of treatments and clinical tests, which are limitations of real-world data. However, these inconsistencies presumably affected all cohorts equally7
![]() Approved indications among the asthma biologics in the analysis vary1,11-13:
Approved indications among the asthma biologics in the analysis vary1,11-13:
- DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment for adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid–dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus1
- Mepolizumab is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment for adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with severe asthma and with an eosinophilic phenotype. Mepolizumab is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus11
- Omalizumab is indicated for adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with persistent moderate-to-severe asthma who have a positive skin test or in vitro reactivity to a perennial aeroallergen and whose symptoms are inadequately controlled with inhaled corticosteroids12
- Limitations of use:
-
Omalizumab is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus
-
Omalizumab is not indicated for treatment of other allergic conditions
-
- Limitations of use:
-
Benralizumab is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with severe asthma, and with an eosinophilic phenotype.
Limitations of Use:
Benralizumab is not indicated for relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus. -
Not all biologics approved in asthma were a part of this study
![]()
This study was sponsored by Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc
Explore the other indications of DUPIXENT
Inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (aged 12+ years)
References: 1. DUPIXENT. Prescribing information. Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; 2024. 2. Wenzel S, Castro M, Corren J, et al. Dupilumab efficacy and safety in adults with uncontrolled persistent asthma despite use of medium-to-high-dose inhaled corticosteroids plus a long-acting β2 agonist: a randomised double-blind placebo-controlled pivotal phase 2b dose-ranging trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10039):31-44. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30307-5 3. Castro M, Rabe KF, Corren J, et al. Dupilumab improves lung function in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma. ERJ Open Res. 2020;6(1):00204-2019. doi:10.1183/23120541.00204-2019 4. Busse WW, Maspero JF, Rabe KF, et al. Liberty Asthma QUEST: phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study to evaluate dupilumab efficacy/safety in patients with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma. Adv Ther. 2018;35(5):737-748. doi:10.1007/s12325-018-0702-4 5. Rabe KF, Nair P, Brusselle G, et al. Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in glucocorticoid-dependent severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(26):2475-2485. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1804093 6. Wechsler ME, Ford LB, Maspero JF, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of dupilumab in patients with moderate-to-severe asthma (TRAVERSE): an open-label extension study. Lancet Respir Med. 2022;10(1):11-25. doi:10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00322-2 7. Data on file. Sanofi US. 8. Bacharier LB, Maspero JF, Katelaris CH, et al. Dupilumab in children with uncontrolled moderate-to-severe asthma. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(24):2230-2240. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2106567 9. Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention, 2023. Global Initiative for Asthma. Updated July 2023. Accessed July 24, 2024. https://ginasthma.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/GINA-2023-Report-WMSA.pdf 10. Bleecker E, Blaiss M, Jacob-Nara J, et al. Real-world effectiveness of dupilumab and other biologics on asthma exacerbations and steroid prescriptions: US-ADVANTAGE study. Poster presented at: American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI) 2022 Annual Scientific Meeting; November 10-14, 2022; Louisville, KY. Poster 8042. 11. Nucala. Prescribing information. GlaxoSmithKline LLC; 2023. 12. Xolair. Prescribing information. Genentech, Inc.; 2023. 13. Fasenra. Prescribing information. AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP; 2021.
INDICATIONS
Atopic Dermatitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD subjects who received DUPIXENT versus placebo, with conjunctivitis being the most frequently reported eye disorder. Conjunctivitis also occurred more frequently in adult CRSwNP subjects, PN subjects, and COPD subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis and keratitis have been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis. Advise patients or their caregivers to report new-onset or worsening eye symptoms. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program and cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD, acute bronchospasm, or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma: Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis: Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, these cases resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT. Advise patients to report new-onset or worsening joint symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Atopic Dermatitis (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia. The safety profile in pediatric patients through Week 16 was similar to that of adults with AD. In an open-label extension study, the long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in pediatric patients observed through Week 52 was consistent with that seen in adults with AD, with hand-foot-and-mouth disease and skin papilloma (incidence ≥2%) reported in patients 6 months to 5 years of age. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
- Asthma (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (incidence ≥1% in adult patients): injection site reactions, eosinophilia, insomnia, toothache, gastritis, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, arthralgia, and herpes viral infections.
- Prurigo Nodularis (incidence ≥2%): nasopharyngitis, conjunctivitis, herpes infection, dizziness, myalgia, and diarrhea.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (incidence ≥2%): viral infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, urinary tract infection, local administration reactions, rhinitis, eosinophilia, toothache, and gastritis.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1‑877‑311‑8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information
INDICATIONS
Atopic Dermatitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD subjects who received DUPIXENT versus placebo, with conjunctivitis being the most frequently reported eye disorder. Conjunctivitis also occurred more frequently in adult CRSwNP subjects, PN subjects, and COPD subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis and keratitis have been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis. Advise patients or their caregivers to report new-onset or worsening eye symptoms. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program and cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD, acute bronchospasm, or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma: Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis: Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, these cases resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT. Advise patients to report new-onset or worsening joint symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Atopic Dermatitis (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia. The safety profile in pediatric patients through Week 16 was similar to that of adults with AD. In an open-label extension study, the long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in pediatric patients observed through Week 52 was consistent with that seen in adults with AD, with hand-foot-and-mouth disease and skin papilloma (incidence ≥2%) reported in patients 6 months to 5 years of age. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
- Asthma (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (incidence ≥1% in adult patients): injection site reactions, eosinophilia, insomnia, toothache, gastritis, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, arthralgia, and herpes viral infections.
- Prurigo Nodularis (incidence ≥2%): nasopharyngitis, conjunctivitis, herpes infection, dizziness, myalgia, and diarrhea.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (incidence ≥2%): viral infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, urinary tract infection, local administration reactions, rhinitis, eosinophilia, toothache, and gastritis.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1‑877‑311‑8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information
INDICATIONS
Atopic Dermatitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 months and older with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis (AD) whose disease is not adequately controlled with topical prescription therapies or when those therapies are not advisable. DUPIXENT can be used with or without topical corticosteroids.
Asthma: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 6 years and older with moderate-to-severe asthma characterized by an eosinophilic phenotype or with oral corticosteroid dependent asthma. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm or status asthmaticus.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with inadequately controlled chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP).
Eosinophilic Esophagitis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 1 year and older, weighing at least 15 kg, with eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE).
Prurigo Nodularis: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prurigo nodularis (PN).
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: DUPIXENT is indicated as an add-on maintenance treatment of adult patients with inadequately controlled chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and an eosinophilic phenotype. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for the relief of acute bronchospasm.
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria: DUPIXENT is indicated for the treatment of adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with chronic spontaneous urticaria (CSU) who remain symptomatic despite H1 antihistamine treatment. Limitations of Use: DUPIXENT is not indicated for treatment of other forms of urticaria.
CONTRAINDICATION: DUPIXENT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to dupilumab or any of its excipients.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity: Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, serum sickness or serum sickness-like reactions, angioedema, generalized urticaria, rash, erythema nodosum, and erythema multiforme have been reported. If a clinically significant hypersensitivity reaction occurs, institute appropriate therapy and discontinue DUPIXENT.
Conjunctivitis and Keratitis: Conjunctivitis and keratitis occurred more frequently in AD subjects who received DUPIXENT versus placebo, with conjunctivitis being the most frequently reported eye disorder. Conjunctivitis also occurred more frequently in adult CRSwNP subjects, PN subjects, and COPD subjects who received DUPIXENT compared to those who received placebo. Conjunctivitis and keratitis have been reported with DUPIXENT in postmarketing settings, predominantly in AD patients. Some patients reported visual disturbances (e.g., blurred vision) associated with conjunctivitis or keratitis. Advise patients or their caregivers to report new-onset or worsening eye symptoms. Consider ophthalmological examination for patients who develop conjunctivitis that does not resolve following standard treatment or signs and symptoms suggestive of keratitis, as appropriate.
Eosinophilic Conditions: Patients being treated for asthma may present with clinical features of eosinophilic pneumonia or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA). These events may be associated with the reduction of oral corticosteroid therapy. Healthcare providers should be alert to vasculitic rash, worsening pulmonary symptoms, cardiac complications, kidney injury, and/or neuropathy presenting in their patients with eosinophilia. Cases of eosinophilic pneumonia were reported in adults who participated in the asthma development program and cases of EGPA have been reported with DUPIXENT in adults who participated in the asthma development program as well as in adults with co-morbid asthma in the CRSwNP development program. Advise patients to report signs of eosinophilic pneumonia and EGPA. Consider withholding DUPIXENT if eosinophilic pneumonia or EGPA are suspected.
Acute Symptoms of Asthma or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or Acute Deteriorating Disease: Do not use DUPIXENT to treat acute symptoms or acute exacerbations of asthma or COPD, acute bronchospasm, or status asthmaticus. Patients should seek medical advice if their asthma or COPD remains uncontrolled or worsens after initiation of DUPIXENT.
Risk Associated with Abrupt Reduction of Corticosteroid Dosage: Do not discontinue systemic, topical, or inhaled corticosteroids abruptly upon initiation of DUPIXENT. Reductions in corticosteroid dose, if appropriate, should be gradual and performed under the direct supervision of a healthcare provider. Reduction in corticosteroid dose may be associated with systemic withdrawal symptoms and/or unmask conditions previously suppressed by systemic corticosteroid therapy.
Patients with Co-morbid Asthma: Advise patients with co-morbid asthma not to adjust or stop their asthma treatments without consultation with their physicians.
Psoriasis: Cases of new-onset psoriasis have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT for the treatment of atopic dermatitis and asthma, including in patients without a family history of psoriasis. In postmarketing reports, these cases resulted in partial or complete resolution of psoriasis with discontinuation of dupilumab, with or without use of supplemental treatment for psoriasis (topical or systemic). Those who continued dupilumab received supplemental treatment for psoriasis to improve associated symptoms. Advise patients to report new-onset psoriasis symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider dermatologic evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Arthralgia and Psoriatic Arthritis: Arthralgia has been reported with the use of DUPIXENT with some patients reporting gait disturbances or decreased mobility associated with joint symptoms; some cases resulted in hospitalization. Cases of new-onset psoriatic arthritis requiring systemic treatment have been reported with the use of DUPIXENT. Advise patients to report new-onset or worsening joint symptoms. If symptoms persist or worsen, consider rheumatological evaluation and/or discontinuation of DUPIXENT.
Parasitic (Helminth) Infections: It is unknown if DUPIXENT will influence the immune response against helminth infections. Treat patients with pre-existing helminth infections before initiating therapy with DUPIXENT. If patients become infected while receiving treatment with DUPIXENT and do not respond to anti-helminth treatment, discontinue treatment with DUPIXENT until the infection resolves. Helminth infections (5 cases of enterobiasis and 1 case of ascariasis) were reported in pediatric patients 6 to 11 years old in the pediatric asthma development program.
Vaccinations: Consider completing all age-appropriate vaccinations as recommended by current immunization guidelines prior to initiating DUPIXENT. Avoid use of live vaccines during treatment with DUPIXENT.
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Atopic Dermatitis (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, conjunctivitis, blepharitis, oral herpes, keratitis, eye pruritus, other herpes simplex virus infection, dry eye, and eosinophilia. The safety profile in pediatric patients through Week 16 was similar to that of adults with AD. In an open-label extension study, the long-term safety profile of DUPIXENT ± TCS in pediatric patients observed through Week 52 was consistent with that seen in adults with AD, with hand-foot-and-mouth disease and skin papilloma (incidence ≥2%) reported in patients 6 months to 5 years of age. These cases did not lead to study drug discontinuation.
- Asthma (incidence ≥1%): injection site reactions, oropharyngeal pain, and eosinophilia.
- Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (incidence ≥1% in adult patients): injection site reactions, eosinophilia, insomnia, toothache, gastritis, arthralgia, and conjunctivitis.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions, upper respiratory tract infections, arthralgia, and herpes viral infections.
- Prurigo Nodularis (incidence ≥2%): nasopharyngitis, conjunctivitis, herpes infection, dizziness, myalgia, and diarrhea.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (incidence ≥2%): viral infection, headache, nasopharyngitis, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, urinary tract infection, local administration reactions, rhinitis, eosinophilia, toothache, and gastritis.
- Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria (incidence ≥2%): injection site reactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Pregnancy: A pregnancy exposure registry monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to DUPIXENT during pregnancy. To enroll or obtain information call 1‑877‑311‑8972 or go to https://mothertobaby.org/ongoing-study/dupixent/. Available data from case reports and case series with DUPIXENT use in pregnant women have not identified a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Human IgG antibodies are known to cross the placental barrier; therefore, DUPIXENT may be transmitted from the mother to the developing fetus.
- Lactation: There are no data on the presence of DUPIXENT in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Maternal IgG is known to be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for DUPIXENT and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from DUPIXENT or from the underlying maternal condition.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information
This site is intended for US payers, formulary committees, or other similar entities for purposes of population-based drug selection, coverage, and/or reimbursement decision-making, pursuant to FD&C Act Section 502(a).
© 2025 Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
DUPIXENT® and DUPIXENT MyWay® are registered trademarks of Sanofi Biotechnology.
Sanofi US is hosting this website on behalf of Sanofi and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Sanofi and Regeneron are industry partners, who are committed to handling personal data in ways that respect your privacy. Both companies may independently process your personal data to manage patient support programs and product marketing campaigns. Please refer to Regeneron’s Privacy Notice and Sanofi’s Privacy Policy and Cookies Policy for more information regarding processing of your personal data.