Cerezyme (imiglucerase): Clinical evidence
Understanding a treatment’s mechanism of action and disease modification capabilities is essential for assessing its true clinical value
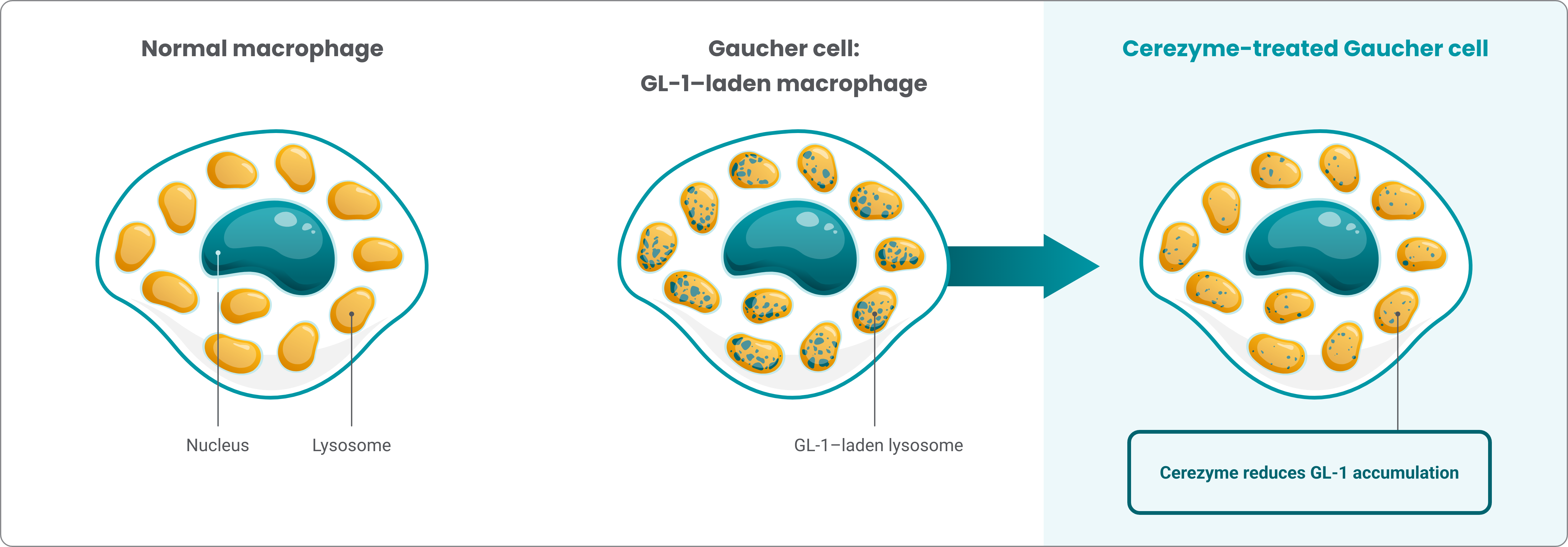
Cerezyme is an analog of the human enzyme β-glucocerebrosidase
(also called acid β-glucosidase)1
Cerezyme reduces the accumulation of glucocerebroside (GL-1) by cleaving the substrate into glucose and ceramide1
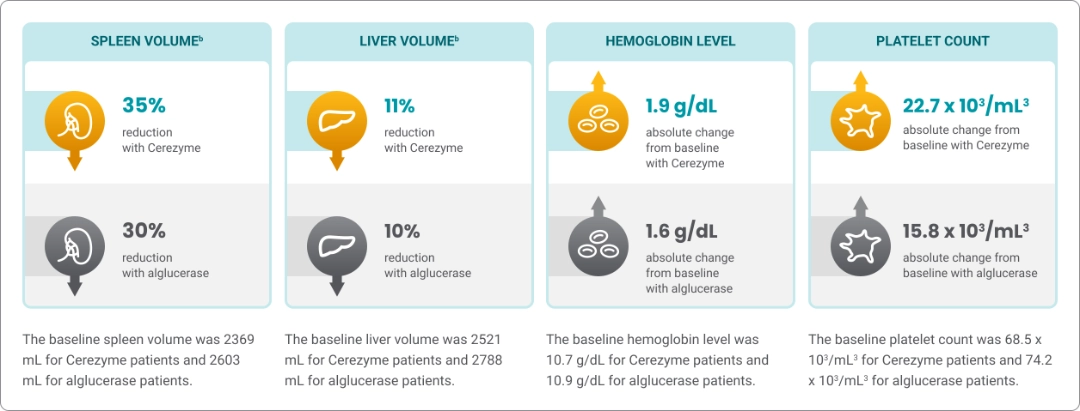
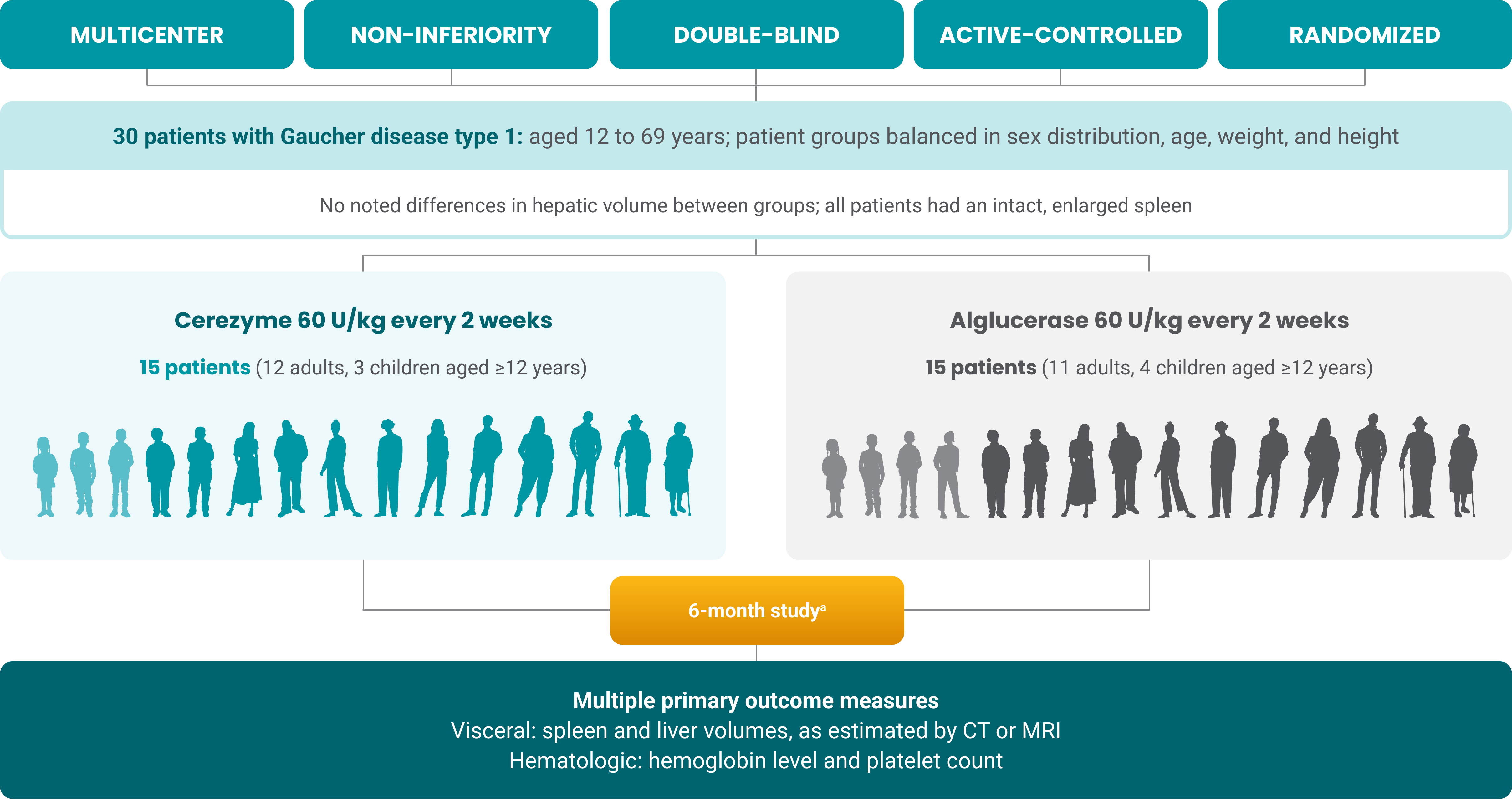
Cerezyme showed improvement in 4 primary efficacy endpoints in patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1)1,a
At the end of the 6-month study period (Cerezyme vs alglucerase, n=15 for each cohort)
Bone x-rays showed improvements in cortical thickness and lucencies in 7 of 11 Cerezyme-treated patients.
aAlglucerase was the first approved enzyme replacement therapy for GD1 and is no longer produced.
bPercentage changes refer to changes from the baseline volume.
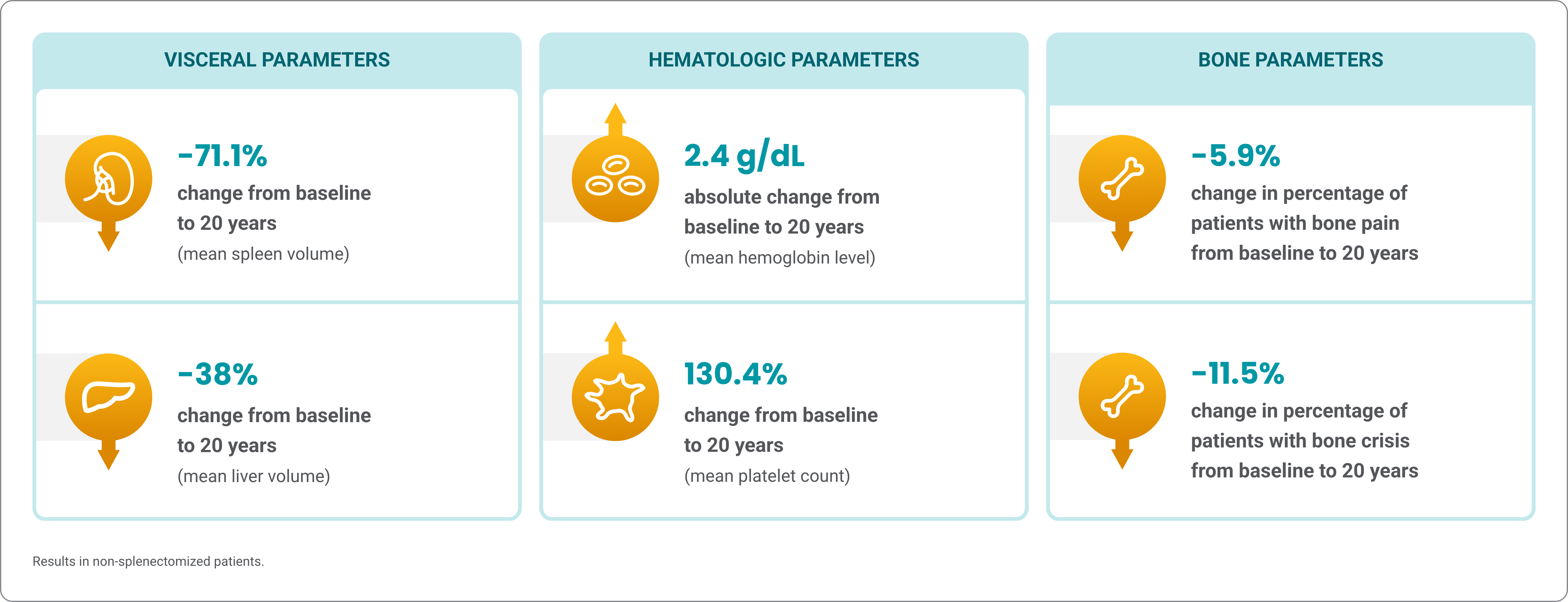
Cerezyme demonstrated improvements in visceral, hematologic, and certain bone parameters over 20 years2,a
A retrospective, observational single-arm study consisted of patients with Gaucher disease type 1 from the ICGG Gaucher Registry2,3
Analysis limitations: Information entry is voluntary and not all the data on every parameter are available for every patient in the registry. The ICGG Gaucher Registry includes patients with a variable range of disease status and management.
Mean changes from baseline at 10 and 20 years, respectively, in splenectomized patients were: in liver volume, 2.3 MN to 1.1 MN and 1.0 MN; in hemoglobin, 11.7 g/dL to 13.3 g/dL and 13.4 g/dL; in platelet count, 229.1 x 109/L to 288.1 x 109/L and 257.0 x 109/L; without bone crisis, 52.2% to 91.3% and 100%; without bone pain, 16.3% to 30.6% and 46.9%.
aThe Cerezyme treatment group from the Gaucher Registry analyses represents patients who received either alglucerase or imiglucerase.
ICGG, International Collaborative Gaucher Group.
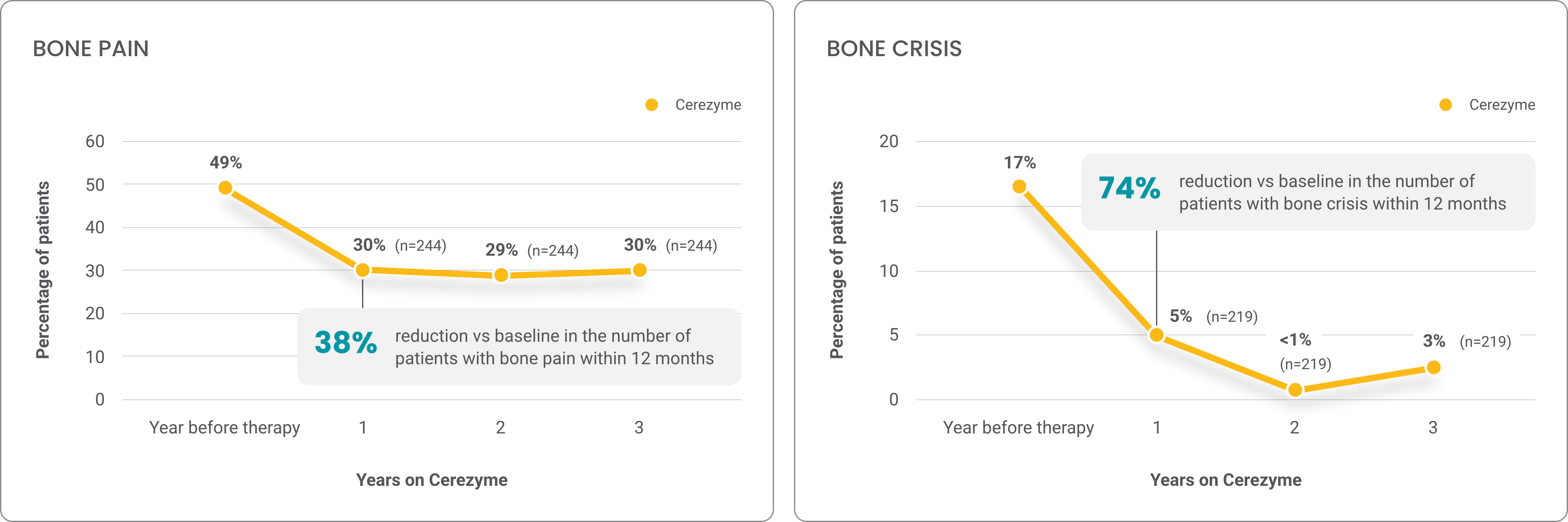
Retrospective analysis of the effect of Cerezyme on the occurrence of bone pain and bone crises over 4 years4
From an ICGG Gaucher Registry study of patients with Gaucher disease type 14
Cerezyme demonstrated safety and efficacy in patients aged 2 years and older5
Use of Cerezyme for this indication is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies of Cerezyme and alglucerase in adults and pediatric patients aged ≥12 years with GD1, with additional data obtained from the medical literature and from postmarketing experience in pediatric patients as young as age 2 years.
The safety and effectiveness in patients younger than age 2 years have not been established.1
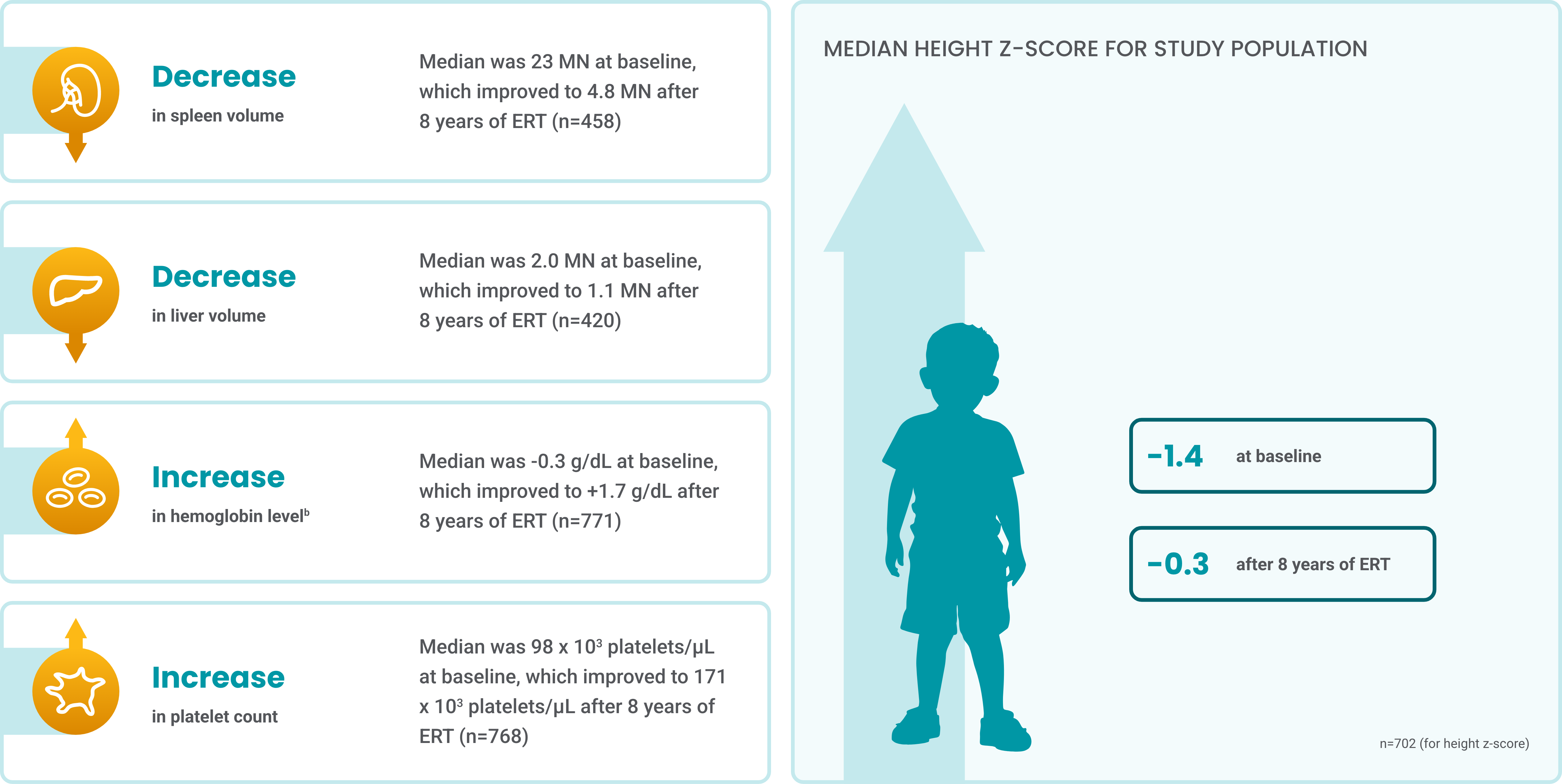
Cerezymea improved long-term visceral and hematologic manifestations in pediatric patients in an 8-year ICGG Gaucher Registry study5
All pediatric patients with GD1 who had undergone partial or total splenectomy were excluded.
aThe Cerezyme treatment group from the Gaucher Registry analyses represents patients with GD1 who received either alglucerase or imiglucerase.
bNormalized hemoglobin levels were analyzed as grams per deciliter below the lower limit of the age- and gender-adjusted reference range.
ERT, enzyme replacement therapy.
Cerezyme safety data1
Adverse reactions
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Cerezyme were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
|
SYSTEM ORGAN CLASS
|
Adverse reactions |
|---|---|
| Nervous system disorders | Dizziness, headache |
| Cardiac disorders | Tachycardia |
| Vascular disorders | Cyanosisa, flushinga, hypotensiona, hypertensiona |
| Respiratory, thoracic, and mediastinal disorders | Cougha, dyspneaa, pneumonia, pulmonary hypertension |
| Gastrointestinal disorders | Abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting |
| Immune system disorders | Anaphylaxisa, hypersensitivity |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders | Angioedemaa, pruritusa, rash, urticariaa |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders | Back pain |
| General disorders and administration-site conditions | Chest discomforta, chills, fatigue, infusion-site burning, infusion-site discomfort, infusion-site swelling, pyrexia |
aSigns and symptoms suggestive of hypersensitivity and other infusion-associated reactions.
Consider periodic monitoring of patients during the first year of treatment for immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody formation
Approximately 15% of patients treated and tested to date have developed IgG antibodies to Cerezyme during the first year of therapy.
- Most patients who developed IgG antibodies did so within 6 months of treatment
- Patients rarely developed antibodies to Cerezyme after 12 months of therapy
Cerezyme dosing and administration1
Cerezyme is administered as an infusion over 1 to 2 hours
- The recommended dosage of Cerezyme, based upon disease severity, ranges from 2.5 units/kg 3 times a week to 60 units/kg once every 2 weeks
- For patients weighing 18 kg and greater, Cerezyme is infused over 1 to 2 hours
- For patients weighing less than 18 kg, Cerezyme is infused over 2 hours
- Dosage may be titrated based on disease manifestations and therapeutic goals for each patient
- Patients who experience hypersensitivity reactions to Cerezyme should be premedicated with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids and monitored for the occurrence of new hypersensitivity reactions. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction occurs, discontinue Cerezyme treatment and initiate appropriate medical treatment

The value of Cerezyme
Several factors may affect the budget impact in Gaucher disease type 1.

Connect with us
Schedule a meeting with a member of the Sanofi Market Access team to learn more about Sanofi products.
References: 1. Cerezyme. Prescribing information. Genzyme Corporation; 2024. 2. Weinreb NJ, Camelo JS Jr, Charrow J, McClain MR, Mistry P, Belmatoug M. Gaucher disease type 1 patients from the ICGG Gaucher Registry sustain initial clinical improvements during twenty years of imiglucerase treatment. Mol Genet Metab. 2021;132(2):100-111. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2020.12.295 3. Data on file. Sanofi US Inc. 2025. 4. Charrow J, Dulisse B, Grabowski GA, Weinreb NJ. The effect of enzyme replacement therapy on bone crisis and bone pain in patients with type 1 Gaucher disease. Clin Genet. 2007;71(3):205-211. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00769.x 5. Andersson H, Kaplan P, Kacena K, Yee J. Eight-year clinical outcomes of long-term enzyme replacement therapy for 884 children with Gaucher disease type 1. Pediatrics. 2008;122(6):1182-1190. doi:10.1542/peds.2007-2144
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
Important Safety Information for Cerezyme:
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for lgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CERDELGA
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
Important Safety Information for Cerezyme:
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for lgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CERDELGA
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
Important Safety Information for Cerezyme:
WARNING: HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS INCLUDING ANAPHYLAXIS
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for lgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CERDELGA
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
This site is intended for US payers only.
© Sanofi. All rights reserved.
Cerezyme and Sanofi are registered trademarks of Sanofi or an affiliate.
CareConnect Personalized Support Services is a trademark of Sanofi or an affiliate.