Gaucher disease: Treatment landscape
About Gaucher disease
Gaucher disease is an inherited condition characterized by the accumulation of glucocerebroside, which results in multiorgan dysfunction.1
General prevalence is believed to be ~1.8 per 100,000 in the US population2
Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) is the most common of 3 Gaucher disease types,* representing 90% of all diagnosed patients in the United States3
Gaucher disease is more common in certain ethnic groups1,4-6
*Gaucher disease types 2 and 3 have primary neuronopathic components not present in GD1.
Disease pathology
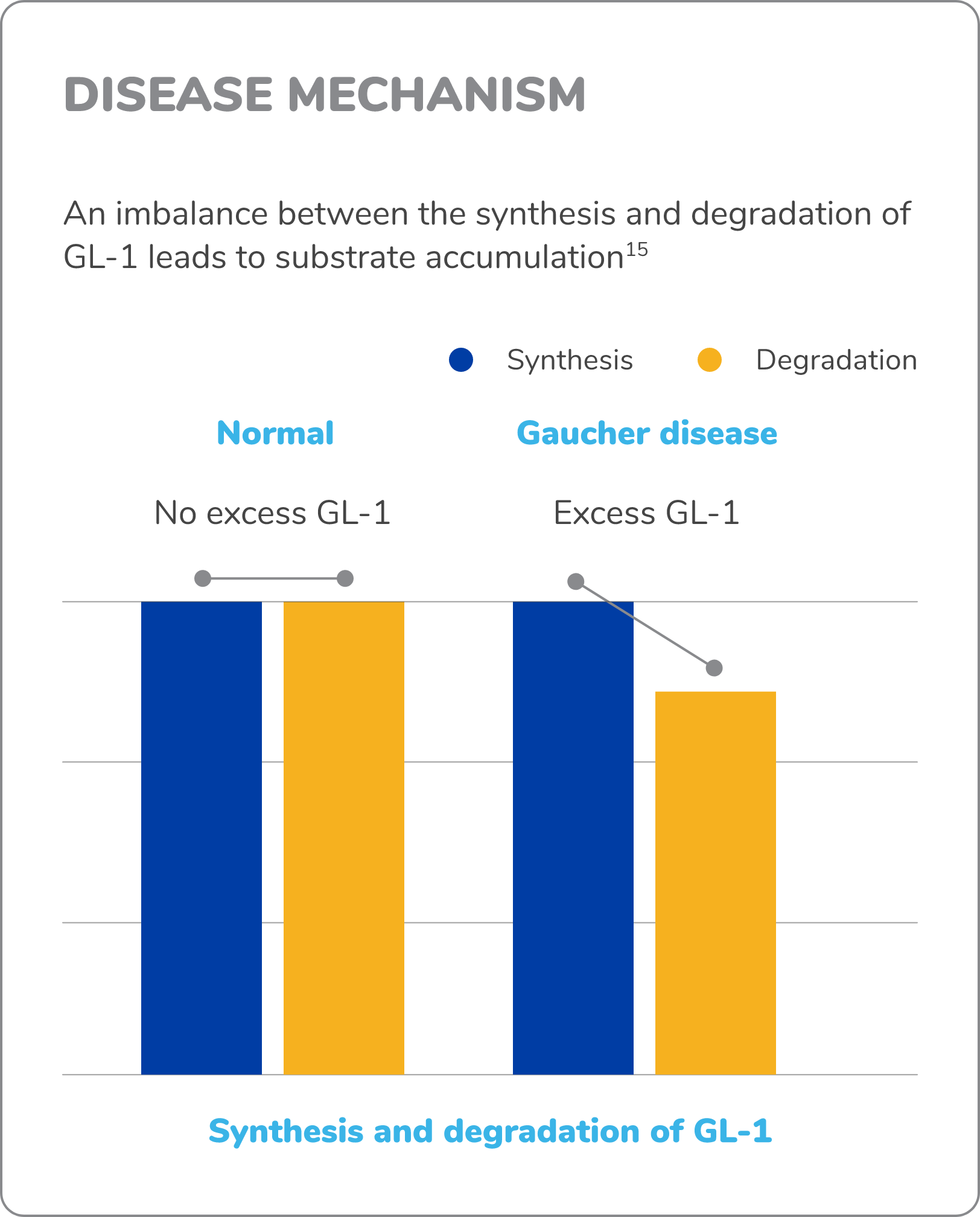
Gaucher disease is caused by pathogenic variants in the GBA1 gene. GBA1 variants result in an enzyme deficiency that inhibits the breakdown of the lipid glucocerebroside (GL-1).5*
GL-1 accumulates in cells, primarily tissue macrophages, that exist in various organ systems.7 Gaucher disease varies widely in range and severity of symptoms,† age of symptom onset, and rate of progression.8
*Glucocerebroside is also known as “glucosylceramide.”3
†Some patients can be asymptomatic.
Multisystemic manifestations
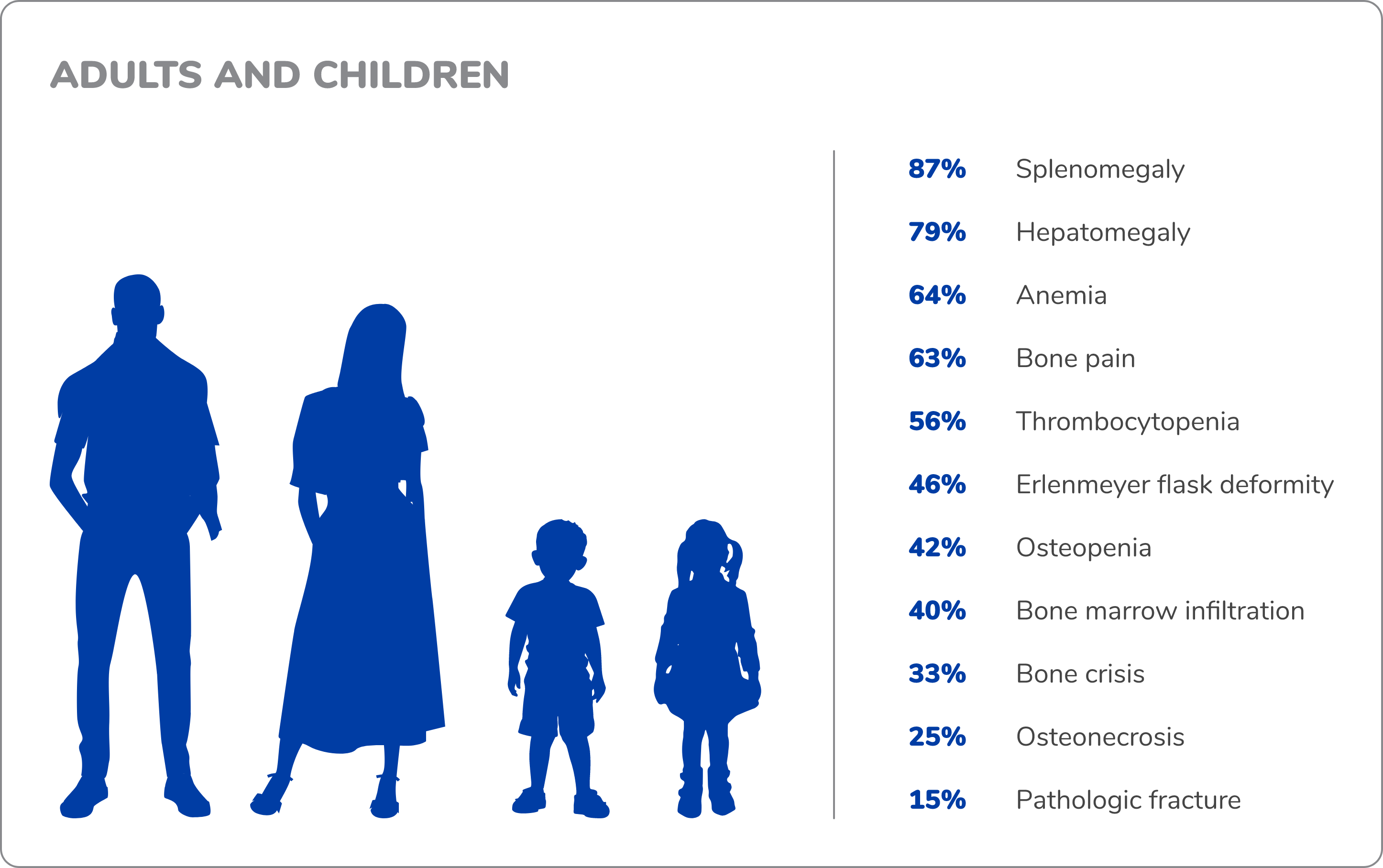
GD1 is marked by debilitating multisystemic manifestations.3
Symptoms vary from patient to patient, but the most common manifestations of GD1 are3,5,9:

Hepatosplenomegaly
The liver and spleen become
enlarged, sometimes leading to
splenic rupture

Cytopenias
Anemia and thrombocytopenia
can result in fatigue, easy
bruising, and excessive bleeding

Skeletal involvement
Macrophages laden with GL-1 can
infiltrate bone marrow; over time,
patients may experience increased
risk of fracture, osteonecrosis, and
severe pain known as “bone crisis”
Burden of disease10,11
Hematologic and visceral complications can be life-threatening, but bone manifestations often result in the greatest morbidity and long-term disability.3,11,12
94% of patients with GD1 show radiologic evidence of bone disease
Over 50% of patients reported chronic bone pain in a Gaucher Registry analysis
Long-range outcomes may include growth delay in pediatric patients and markedly reduced quality of life
The consequences of long-term disease progression may be mitigated by timely diagnosis and treatment.1,8,13,14
Healthcare providers test for Gaucher disease using an enzyme assay to determine acid beta-glucosidase deficiency
Genetic testing may be used to confirm diagnosis or to determine if a family member or a prospective parent is a carrier
Early intervention can be key to potentially avoiding severe, irreversible bone damage and other organ complications
In a disease as variable as GD1, healthcare providers require multiple options to address a variety of patient treatment goals
References: 1. Mistry PK, Cappellini MD, Lukina E, et al. A reappraisal of Gaucher disease—diagnosis and disease management algorithms. Am J Hematol. 2011;86(1):110-115. doi:10.1002/ajh.21888 2. Rossi C, Ferrante R, Valentinuzzi S, et al. Noninvasive DBS-based approaches to assist clinical diagnosis and treatment monitoring of Gaucher disease. Biomedicines. 2023;11(10):2672. doi:10.3390/biomedicines11102672 3. Pastores GM, Weinreb NJ, Aerts H, et al. Therapeutic goals in the treatment of Gaucher disease. Semin Hematol. 2004;41(suppl 5):4-14. doi:10.1053/j.seminhematol.2004.07.009 4. Nalysnyk L, Sugarman R, Cele C, Uyei J, Ward A. Budget impact analysis of eliglustat for the treatment of Gaucher disease type 1 in the United States. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2018;24(10):1002-1008. doi:10.18553/jmcp.2018.24.10.1002 5. Stone WL, Basit H, Mukkamalla SKR, Master SR. Gaucher disease. StatPearls. January 2024. Updated November 12, 2023. Accessed June 25, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK448080/ 6. Ostrer H. A genetic profile of contemporary Jewish populations. Nat Rev Genet. 2001;2(11):891-898. doi:10.1038/35098506 7. Dekker N, van Dussen L, Hollak CEM, et al. Elevated plasma glucosylsphingosine in Gaucher disease: relation to phenotype, storage cell markers, and therapeutic response. Blood. 2011;118(16):e118-e127. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-05-352971 8. Wilson A, Chiorean A, Aguiar M, et al. Development of a rare disease algorithm to identify persons at risk of Gaucher disease using electronic health records in the United States. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2023;18(1):280. doi:10.1186/s13023-023-02868-2 9. Cox TM, Charrow J, Lukina E, Mistry PK, Foster MC, Peterschmitt MJ. Long-term effects of eliglustat on skeletal manifestations in clinical trials of patients with Gaucher disease type 1. Genet Med. 2023;25(2):100329. doi:10.1016/j.gim.2022.10.011 10. Kaplan P, Andersson HC, Kacena KA, Yee JD. The clinical and demographic characteristics of nonneuronopathic Gaucher disease in 887 children at diagnosis. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2006;160(6):603-608. doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.6.603 11. Charrow J, Andersson HC, Kaplan P, et al. The Gaucher Registry: demographics and disease characteristics of 1698 patients with Gaucher disease. Arch Intern Med. 2000;160(18):2835-2843. doi:10.1001/archinte.160.18.2835 12. Charrow J, Dulisse B, Grabowski GA, Weinreb NJ. The effect of enzyme replacement therapy on bone crisis and bone pain in patients with type 1 Gaucher disease. Clin Genet. 2007;71(3):205-211. doi:10.1111/j.1399-0004.2007.00769.x 13. Gaucher disease. National Organization for Rare Disorders. Updated March 3, 2020. Accessed February 2, 2024. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/gaucher-disease/ 14. Mistry PK, Sadan S, Yang R, Yee J, Yang M. Consequences of diagnostic delays in type 1 Gaucher disease: the need for greater awareness among hematologists-oncologists and an opportunity for early diagnosis and intervention. Am J Hematol. 2007;82(8):697-701. doi:10.1002/ajh.20908 15. Ivanova M. Altered sphingolipids metabolism damaged mitochondrial functions: lessons learned from Gaucher and Fabry diseases. J Clin Med. 2020;9(4):1116. doi:10.3390/jcm9041116 16. Hughes DA, Pastores GM. Gaucher disease. In: Adam MP, Feldman J, Mirzaa GM, et al, eds. GeneReviews®. July 27, 2000. Updated December 7, 2023. Accessed March 7, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1269/
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CEREZYME
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
Warnings and Precautions:
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for IgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CEREZYME
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
Warnings and Precautions:
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for IgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
INDICATION FOR CERDELGA
CERDELGA is indicated for the long-term treatment of adult patients with Gaucher disease type 1 (GD1) who are CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs), intermediate metabolizers (IMs), or poor metabolizers (PMs) as detected by an FDA-cleared test.
Limitations of Use:
- Patients who are CYP2D6 ultra-rapid metabolizers (URMs) may not achieve adequate concentrations of CERDELGA to achieve a therapeutic effect.
- A specific dosage cannot be recommended for those patients whose CYP2D6 genotype cannot be determined (indeterminate metabolizers).
INDICATION FOR CEREZYME
Cerezyme® (imiglucerase) for injection is indicated for treatment of adults and pediatric patients 2 years of age and older with Type 1 Gaucher disease that results in one or more of the following conditions:
- anemia
- thrombocytopenia
- bone disease
- hepatomegaly or splenomegaly
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CERDELGA is contraindicated in the following patients based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongation of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac intervals:
- Extensive Metabolizers (EMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, EMs with moderate or severe hepatic impairment, or EMs with mild hepatic impairment and taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor.
- Intermediate Metabolizers (IMs) taking a strong or moderate CYP2D6 inhibitor concomitantly with a strong or moderate CYP3A inhibitor, IMs taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or IMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
- Poor Metabolizers (PMs) taking a strong CYP3A inhibitor, or PMs with any degree of hepatic impairment.
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
CERDELGA is predicted to cause increases in ECG intervals (PR, QTc, and QRS) at substantially elevated plasma concentrations and may increase risk of cardiac arrhythmias. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or requires dosage adjustment in patients taking CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, depending on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, type of inhibitor, or degree of hepatic impairment. Avoid use of CERDELGA in patients with pre-existing cardiac disease, long QT syndrome, or in combination with Class IA or Class III antiarrhythmic medications.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (≥10%) to CERDELGA include: fatigue, headache, nausea, diarrhea, back pain, pain in extremities, and upper abdominal pain.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Coadministration of CERDELGA with CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors may increase eliglustat concentrations, which may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmias from prolongations of the PR, QTc, and/or QRS cardiac interval. Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated, to be avoided, or may require dosage adjustment depending on the concomitant drug and CYP2D6 metabolizer status. See section 7 of the full Prescribing Information for more details and other potentially significant drug interactions.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Available data on the use of CERDELGA in pregnant women is not sufficient to assess drug-associated risks of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CERDELGA and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from CERDELGA or from the underlying maternal condition.
Use of CERDELGA in patients with renal impairment is based on the patient’s CYP2D6 metabolizer status. Avoid use of CERDELGA in EMs with end-stage renal disease (ESRD), and IMs and PMs with any degree of renal impairment.
Use of CERDELGA is contraindicated or may require dosage adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment based on CYP2D6 metabolizer status, concomitant use of CYP2D6 or CYP3A inhibitors, and degree of hepatic impairment.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION FOR CEREZYME
Patients treated with enzyme replacement therapies have experienced life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis. Anaphylaxis has occurred during the early course of enzyme replacement therapy and after extended duration of therapy.
Initiate CEREZYME in a healthcare setting with appropriate medical monitoring and support measures, including access to cardiopulmonary resuscitation equipment. If a severe hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) occurs, discontinue CEREZYME and immediately initiate appropriate medical treatment, including use of epinephrine. Inform patients of the symptoms of life-threatening hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, and to seek immediate medical care should symptoms occur.
Warnings and Precautions:
Hypersensitivity Reactions Including Anaphylaxis: See Boxed WARNING.
Patients with antibody to imiglucerase have a higher risk of hypersensitivity reactions. Consider periodic monitoring during the first year of treatment for IgG antibody formation.
Consider risks and benefits of readministering Cerezyme to individual patients following a severe reaction. Consider reducing the rate of infusion, pretreat with antihistamines and/or corticosteroids, and monitor patients for new signs and symptoms of a severe hypersensitivity reaction.
Infusion-Associated Reactions:
Infusion associated reactions (IARs) have been observed in patients treated with Cerezyme. If an IAR occurs, decreasing the infusion rate, temporarily stopping the infusion and/or administering antihistamines and/or antipyretics may ameliorate the symptoms. Closely monitor patients who have experienced IARs when re-administering Cerezyme.
Adverse Reactions:
- Adverse reactions reported in adults include back pain, chills, dizziness, fatigue, headache, hypersensitivity reactions, nausea, pyrexia, and vomiting.
- Adverse reactions reported in pediatric patients 2 years of age and older are similar to adults.
Please see Full Prescribing Information, including Boxed WARNING.
This site is intended for US payers only.
© Sanofi. All rights reserved.
Cerdelga and Sanofi are registered trademarks of Sanofi or an affiliate.
CareConnect Personalized Support Services is a trademark of Sanofi or an affiliate.